Touch Screen Panel
Touch Screen Panel (TSP) refers to a device that identifies coordinates of the exact place when pressing or touching the display screen. Smartphones that we commonly use features touch screen panel, so we can pilot our smartphones by touching the screen without separate external buttons.
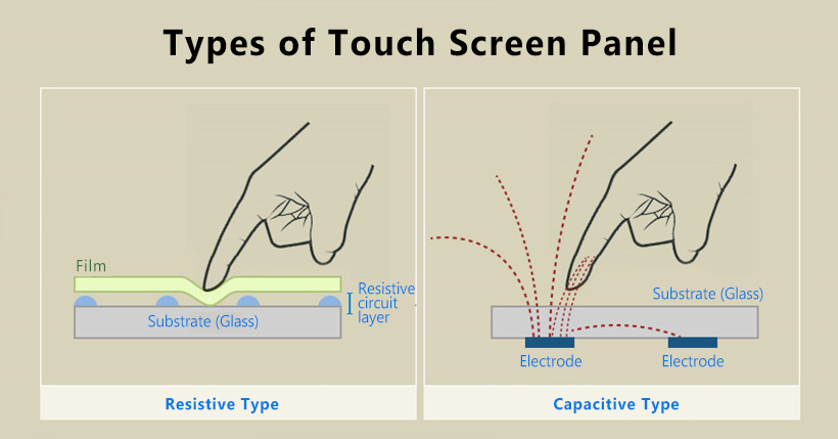
The type of touch screen panels varies depending on how they work, such as capacitive touch, resistive touch, infrared ray touch, and acoustic wave touch. Early smartphones adopted a resistive which operates by the pressure applied. This method recognizes users’ touch when upper and lower substrates are in contact due to external pressure. As a result, this method comes with the disadvantage of a low touch recognition rate since it requires pressure hard enough to have films contact.
Meanwhile, most of the latest smartphones use capacitive-type touch screen panels. This method detects the change in capacitance of the electric conductor, such as a human hand, as soon as it touches the touch screen. Likewise, the capacitive type has good touch sensitivity and befits small and medium-sized models, so most mobile devices adopt it.
Touch screen panels are divided into external and embedded types according to the panel structure. The external type attaches a TSP film to the outside of the display panel, and the embedded type integrates the touch screen feature inside the panel.
Recently, the embedded type has been mainly used to make the panel thinner than the external type and reduce light reflection on the touch panel surface. In particular, the On Cell Type used in OLEDs has merits in terms of thickness and light transmittance as it embeds a touch sensor on the upper substrate of the display.
Flexible Printed Circuit Board
To operate a display panel, IT devices like smartphones send a signal first which images should be displayed. Application Processor (AP), which is similar to the Central processing unit (CPU) of PC, is a system on a chip (SoC) designed to support applications running in a mobile operating system. The application processor determines and sends signals, and Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) is the first component that transports the commanded signal to the display panel.
To understand FPCB better, you first need to know what Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is. Printed circuit board is a circuit component that transports electric signals, and in human terms, it is compared to a nerve. PCB is the primary component widely used in most electric devices, from home appliances to up-to-date mobile communication devices such as smartphones.
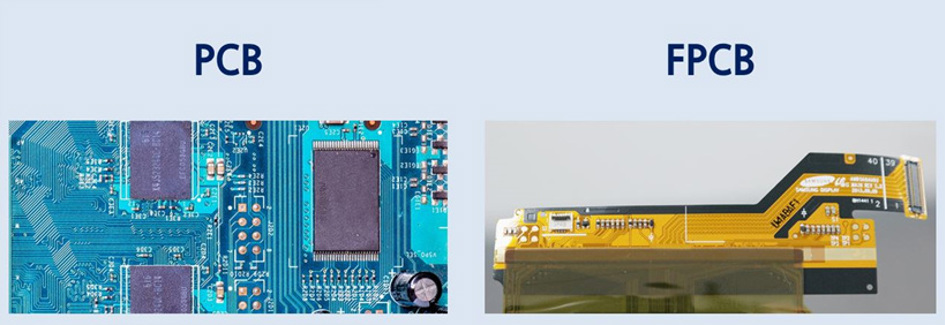
Flexible Printed Circuit Board is one of the types of PCB that converted its characteristic from conventional hard PCB to flexible circuit board. When it comes to mobile devices, it has been developed to minimize the sizes to have better portability. For portable devices, the PCB should attach being folded to the backside of the display panel, and thus it requires the characterization of thin and bendable.
Unlike Display Driver IC (DDI), FPCB doesn’t work independently, so that the key function of FPCB is to send a commanded signal from the application processor to display driver IC.
Thanks to the flexibility and lightness, FPCB improves the spatial advantage. It has become an essential part in the era that unveiled mobile devices with various types of form factors.
This article is adapted from the Learn Display series on the Samsung Display Newsroom. Here is the original article about touch screen panels and here is the original article about flexible printed circuit board. They are only reproduced here with the kind permission of Samsung Display Newsroom.

